590 Dgrid_FPU
590 : Dgrid_FPU
- Author: Aravind-Prasad-Abhinav-Prakash
- Description: 4 Input FPU for MAC at 40MHZ
- GitHub repository
- Clock: 40000000 Hz
How it works
The Dgrid_FPU (Floating Point Unit) is an integral component of computer hardware engineered to execute floating-point arithmetic operations. It features four 32-bit inputs organized to conduct dual multiplications followed by an addition in series. Specifically, the first pair of 32-bit inputs is multiplied, and simultaneously, the second pair is processed similarly. The results from these multiplications are then fed into a two-input adder, producing a 32-bit final output. This configuration is highly effective in applications that demand robust computing capabilities, such as high-performance computing, digital signal processing, scientific simulations, and graphics processing. The Dgrid_FPU's architecture, which enables the parallel processing of multiple arithmetic operations, significantly boosts performance in these computationally intensive tasks.
32bit I\P 32bit I\P 32bit I\P 32bit I\P
| | | |
---------------------- ----------------------
\ / \ /
\ FPU / \ FPU /
\ MULTIPLIER / \ MULTIPLIER /
\ / \ /
-------------- --------------
|___________ ________________|
32bit| | 32bit
----------------------
\ /
\ FPU /
\ ADDER /
\ /
--------------
|
32bit O\P
The Dgrid_FPU top module is designed with a configuration that supports 8-bit input and output interfaces, necessitating a systematic process to handle the 128-bit data (comprising four 32-bit inputs) required for operations. The input process involves 16 clock cycles to load the four 32-bit registers sequentially. Once the data is loaded, the computation begins, producing a 32-bit output over the subsequent two clock cycles.
After the computation phase, the 32-bit result is output through the 8-bit interface, which requires an additional four clock cycles to read out the data thoroughly. Additionally, two clock cycles are utilized for data transfer, bringing the total cycle count to 24 for an entire operation sequence from input loading to output retrieval.
A reset operation is required to prepare the module for a new data set, ensuring that the Dgrid_FPU is ready to process subsequent inputs efficiently. It is important to note that both the input and output data conform to the IEEE 754 standard for floating-point numbers, ensuring compatibility and precision in high-stake computational applications.
This Verilog code outlines a Floating Point Unit (FPU) for use in Machine Arithmetic Cores (MACs) within AI accelerators. The FPU facilitates key operations such as adding and multiplying floating-point numbers, which are crucial for executing complex mathematical computations in AI algorithms. It includes modules for managing data input and output, processing up to 128-bit and 32-bit registers, and handling edge cases like infinity and zero. This architecture is especially beneficial for AI applications, allowing parallel processing and enhancing computational efficiency and precision in neural networks. By accelerating operations and ensuring robust data handling, this FPU is instrumental in optimizing AI accelerators, ultimately speeding up learning and inference processes.
How to test
To effectively test the Dgrid_FPU, follow these step-by-step instructions:
- Reset the Circuit: Initiate by resetting the circuit to clear any previous data and prepare it for new input.
- Write Data: Write a 128-bit bitstream that includes all four inputs, entering the data 8 bits at a time. This step requires 16 clock cycles to complete.
- Wait for Computation: Allow the module to process the inputs, which will take up to the 20th clock cycle.
- Read Output Data: From the 21st to the 24th clock cycle, read out the 32-bit result in increments of 8 bits to verify the output and ensure the system's functionality.
Example
-
I1 = 2.2 (HEX - 400ccccd)
-
I2 = 3.3 (HEX - 40533333)
-
I2 = 4.4 (HEX - 408ccccd)
-
I2 = 5.5 (HEX - 40b00000)
-
FINAL OUTPUT = 31.46 (HEX - 41fbae13)
Then the bitstream will be 400ccccd_40533333_408ccccd_40b00000 and start sending it from LHS e.g. - Fist data to be send is 40 and last data is 00 and then observe the output.
Waveform
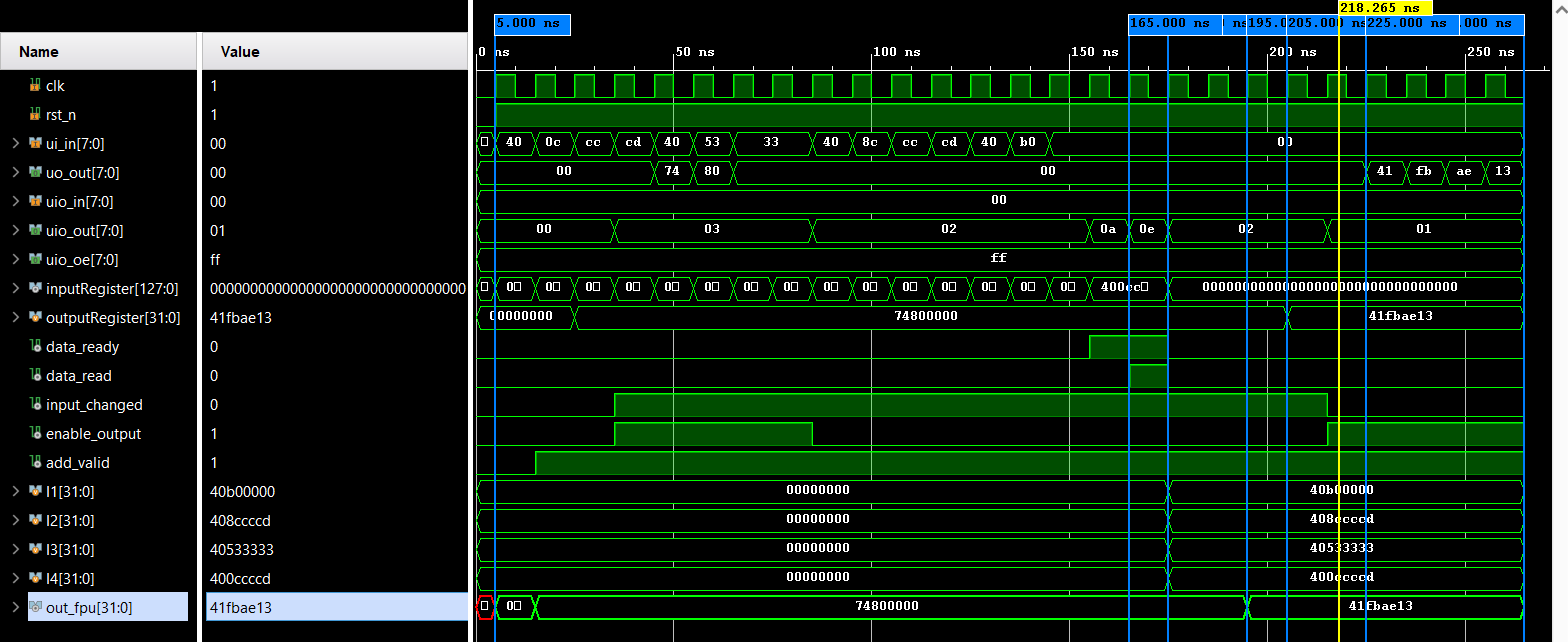
IO
| # | Input | Output | Bidirectional |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Bit 0 Input | Bit 0 Output | Output used as valid Signal |
| 1 | Bit 1 Input | Bit 1 Output | Output used as valid Signal |
| 2 | Bit 2 Input | Bit 2 Output | Output used as valid Signal |
| 3 | Bit 3 Input | Bit 3 Output | Output used as valid Signal |
| 4 | Bit 4 Input | Bit 4 Output | 0 |
| 5 | Bit 5 Input | Bit 5 Output | 0 |
| 6 | Bit 6 Input | Bit 6 Output | 0 |
| 7 | Bit 7 Input | Bit 7 Output | 0 |